Introduction to Gear Couplings
Gear couplings are mechanical devices designed to transmit torque between two shafts while accommodating misalignment. Widely used in industrial machinery, they provide a reliable connection that ensures smooth rotational motion. Their design combines durability with flexibility, making them ideal for high-speed and high-torque applications. Proper selection, installation, and maintenance are critical for maximizing their lifespan and efficiency.
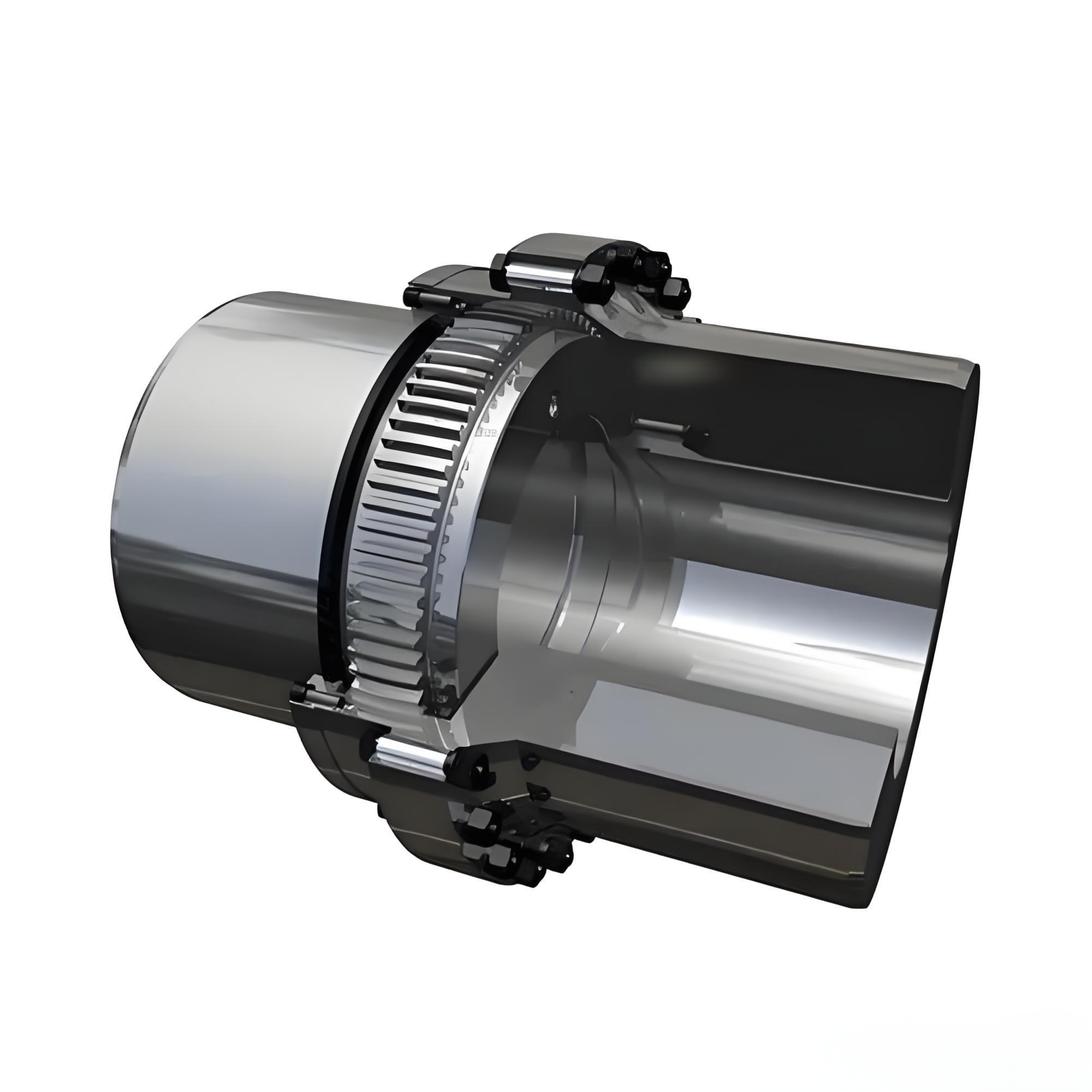

Design Principles of Gear Couplings
The core of a gear coupling consists of two hubs with external teeth and a sleeve with internal teeth that mesh with the hubs. This design allows the coupling to transmit high torque while accommodating angular, parallel, and axial misalignment. Gear couplings are usually made from high-strength alloy steel and may be hardened or coated to improve wear resistance.
Types of Gear Couplings
Gear couplings are broadly categorized based on their flexibility and configuration:
- Rigid Gear Couplings: Provide precise torque transmission with minimal flexibility, suitable for aligned shafts.
- Flexible Gear Couplings: Accommodate angular, parallel, and axial misalignment, reducing stress on connected machinery.
- External Gear Couplings: The hub teeth are on the outside, meshing with an internal sleeve; commonly used in high-speed applications.
- Internal Gear Couplings: The hub teeth are internal, meshing with an external sleeve; beneficial for compact machinery layouts.
Industrial Applications of Gear Couplings
Gear couplings are integral components in various industrial sectors due to their high torque capacity and ability to handle misalignment. Industries such as power generation, mining, steel, and pulp and paper rely heavily on them for reliable operation of heavy machinery.
Power Generation
In power plants, gear couplings connect turbines to generators. They are preferred because they can handle high rotational speeds while minimizing backlash and vibration. Flexible gear couplings also protect expensive machinery from misalignment caused by thermal expansion.
Mining and Material Handling
Mining equipment such as crushers, conveyors, and mills requires gear couplings to transmit high torque efficiently. Flexible couplings accommodate shaft misalignment caused by uneven terrain or heavy loads, preventing damage to the machinery.
Steel and Pulp Industries
In steel rolling mills and pulp processing machinery, gear couplings handle the intense mechanical stress of high-torque operations. Proper lubrication and alignment ensure smooth performance and reduce downtime.
Benefits of Using Gear Couplings
Gear couplings offer several advantages over other types of couplings, making them a preferred choice in demanding applications:
- High Torque Capacity: Ideal for heavy-duty machinery.
- Misalignment Compensation: Reduces stress on connected equipment.
- Durability: Made from hardened alloys to resist wear and fatigue.
- Compact Design: Allows installation in tight spaces without sacrificing performance.
- Maintenance-Friendly: Modular design allows replacement of hubs or sleeves individually.
Installation and Alignment Tips
Proper installation is critical for the optimal performance of gear couplings. Misalignment, improper lubrication, or loose fittings can significantly reduce the service life.
Alignment Techniques
To ensure efficient torque transmission:
- Use dial indicators or laser alignment tools to achieve precise alignment.
- Ensure that both shafts are parallel and angular misalignment is within manufacturer tolerances.
- Allow for thermal expansion and axial movement during operation.
Lubrication Practices
Lubrication is critical for reducing wear between the gear teeth. Common practices include:
- Grease Lubrication: Suitable for low to medium-speed applications; reapply regularly based on usage.
- Oil Bath Lubrication: Ideal for high-speed or heavily loaded couplings; ensures continuous lubrication of teeth.
- Monitor for Contamination: Dust, moisture, or debris can accelerate wear and must be minimized.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance ensures the longevity and reliability of gear couplings. The following practices help prevent unexpected failures:
Inspection Guidelines
Check for the following during routine inspections:
- Wear on gear teeth or sleeve components.
- Excessive backlash or looseness in hubs.
- Lubrication quality and quantity.
- Signs of corrosion or pitting on mating surfaces.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Common problems and corrective actions include:
| Issue | Cause | Solution |
| Excessive vibration | Misalignment or worn teeth | Realign shafts, replace damaged hubs |
| Overheating | Insufficient lubrication | Check lubrication schedule, apply proper grease/oil |
| Noise during operation | Debris or dry gear teeth | Clean coupling, ensure proper lubrication |
Choosing the Right Gear Coupling
Selecting the appropriate gear coupling depends on the application's torque, speed, and misalignment requirements. Consider the following factors:
- Torque capacity and service factor based on load conditions.
- Permissible angular, parallel, and axial misalignment.
- Operating environment: temperature, dust, moisture, and chemical exposure.
- Ease of maintenance and availability of replacement parts.
Conclusion
Gear couplings are indispensable components in high-performance industrial machinery, providing efficient torque transmission while compensating for misalignment. Understanding their design, applications, installation, and maintenance practices ensures reliability, reduces downtime, and maximizes the lifespan of critical equipment. By selecting the right type and maintaining it properly, industries can achieve optimal performance and protect their machinery investments.






 English
English русский
русский
