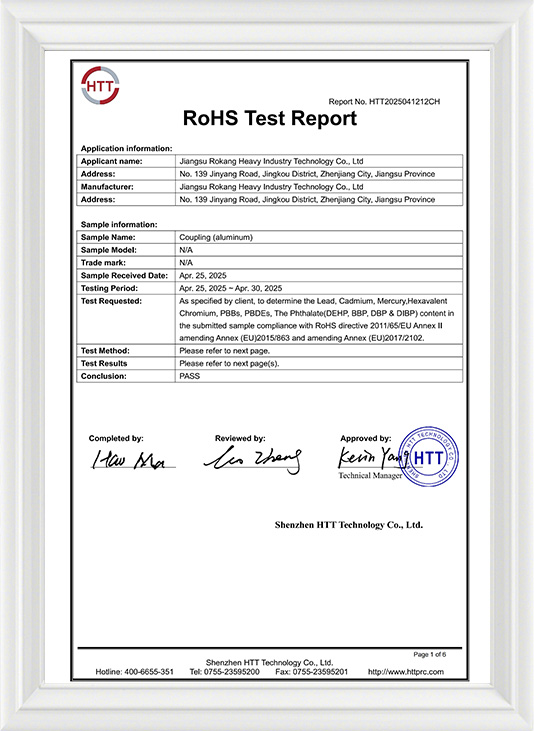
Jiangsu Rokang Heavy Industry Technology Co., Ltd.
Jiangsu Rokang Heavy Industry Technology Co., Ltd. has fixed assets of more than 80 million yuan, and has a team of professional talents in mechanical design, precision manufacturing, heat treatment, welding, etc.; the company has a one-stop complete set of processing facilities and a series of quality inspection systems such as measurement, physical and chemical, and dynamic testing, and has a comprehensive mechanical processing capability.
Constant Velocity Joints Manufacturers and
CV Joints Factory in China.
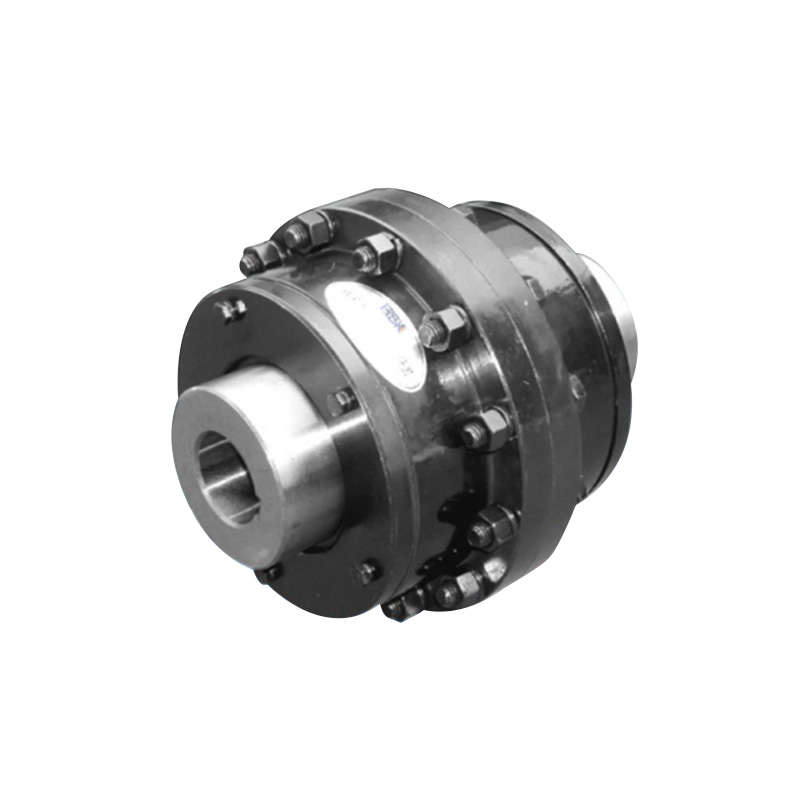
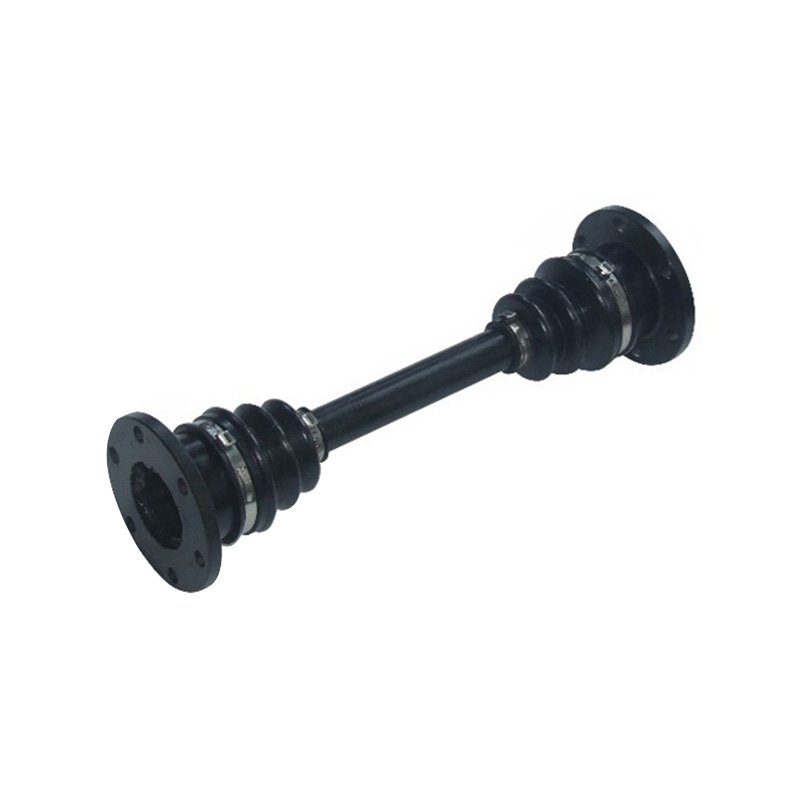
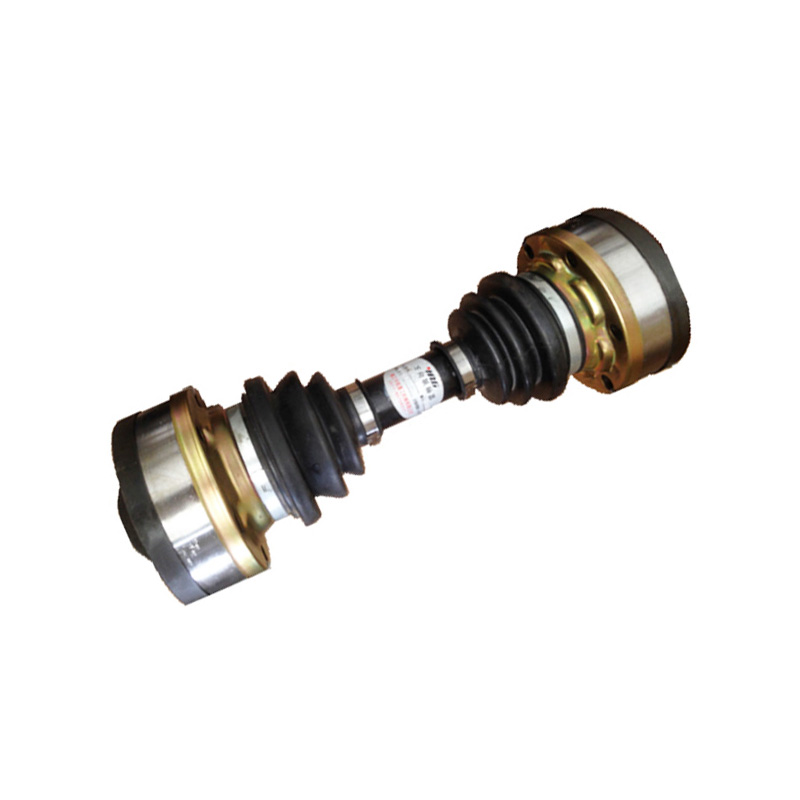
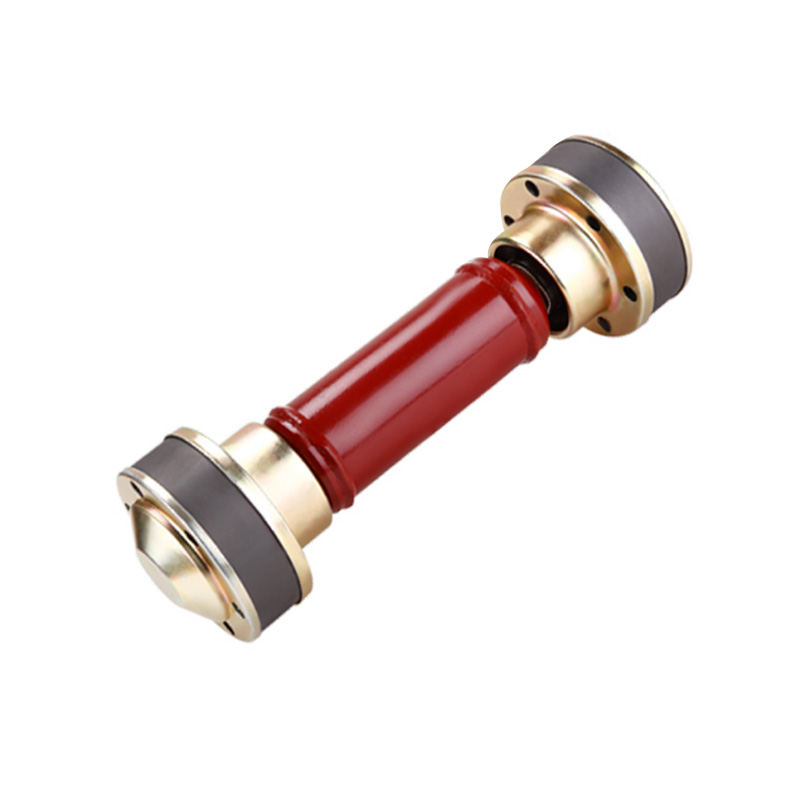
For many years, the company has been committed to the research and development and manufacturing of ball cage type constant velocity universal couplings, cross shaft type universal couplings, and drum gear couplings. It has carried out close industry-university-research cooperation with military and local scientific research institutes and Power Engineering Department of PLA Naval Academy, and has continuously expanded into the fields of precision, heavy load and high speed. The products have successfully replaced foreign famous brand products with excellent performance, and the process technology has reached the international advanced level. It has been widely used in lifting and transportation, metallurgical machinery, metal rolling, engineering machinery, mining machinery, petrochemical, textile machinery, military ships, armored vehicles, railway locomotives, special vehicles and other fields. The product quality and service have been recognized and praised by the majority of users, and are exported to Europe, America, Russia, the Middle East, India and other countries and regions.
In recent years, the company has been committed to the in-depth research and development of ball cage constant velocity universal couplings, and has successively developed ball cage constant velocity universal couplings for screw pumps, ball spline ball cage constant velocity universal couplings, coaxial double-speed, and double-way ball cage constant velocity universal couplings.
Custom Constant Velocity Joints for Industrial Machines. It fundamentally solves the new problems that users currently encounter during use. The company has always adhered to the business purpose of "quality first, honest management, and customer first". We are willing to work with you with excellent products, preferential prices and thoughtful services to create a brilliant career!






 English
English русский
русский