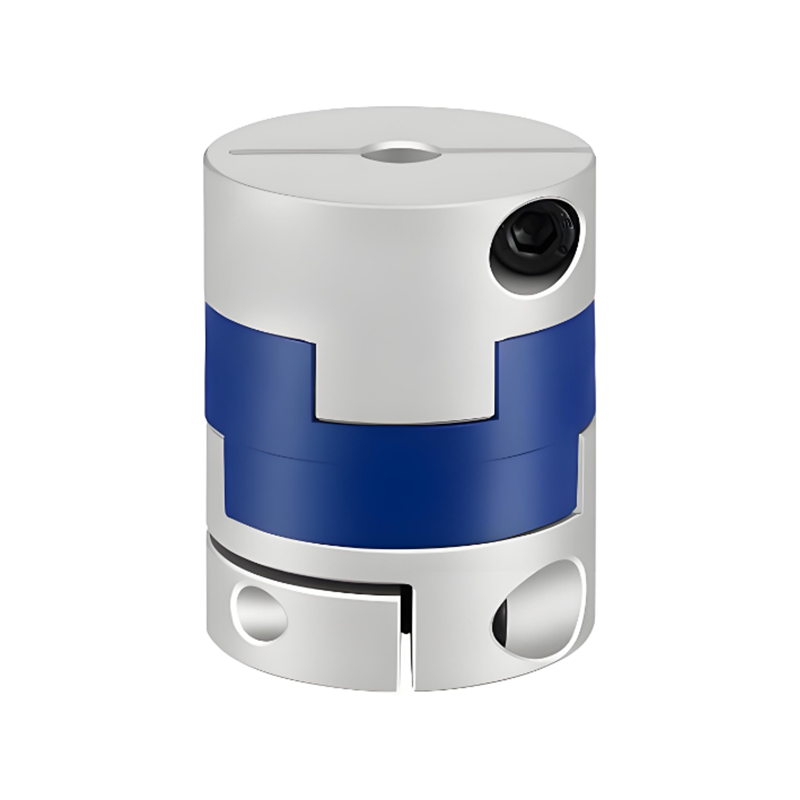
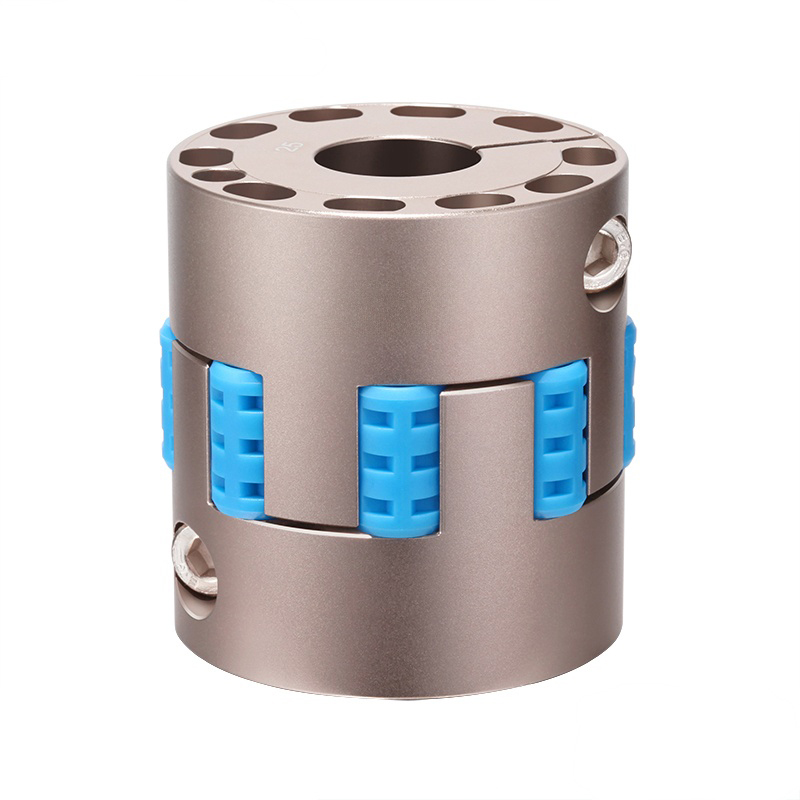
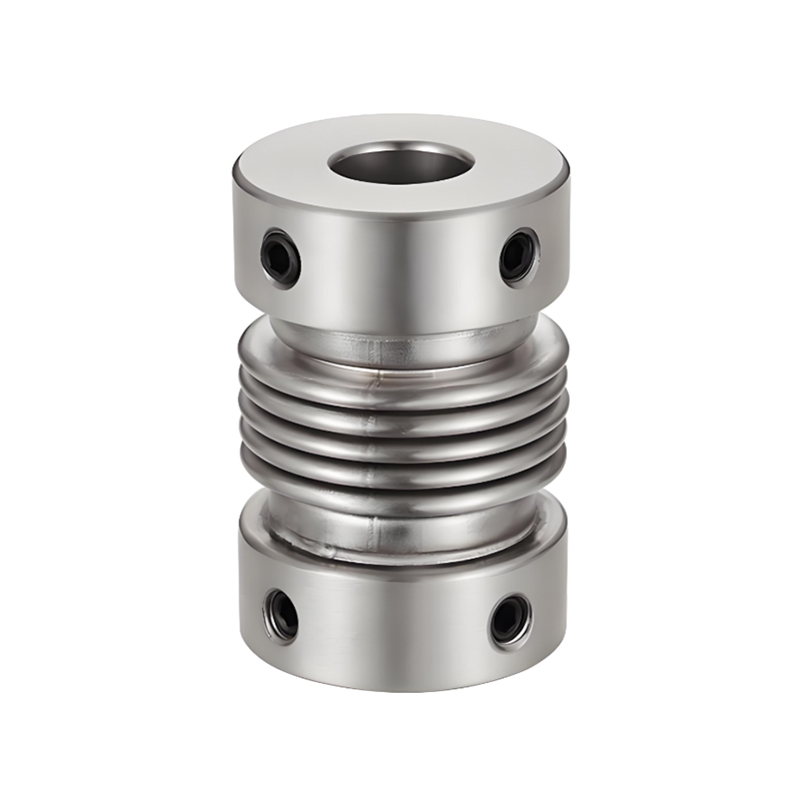
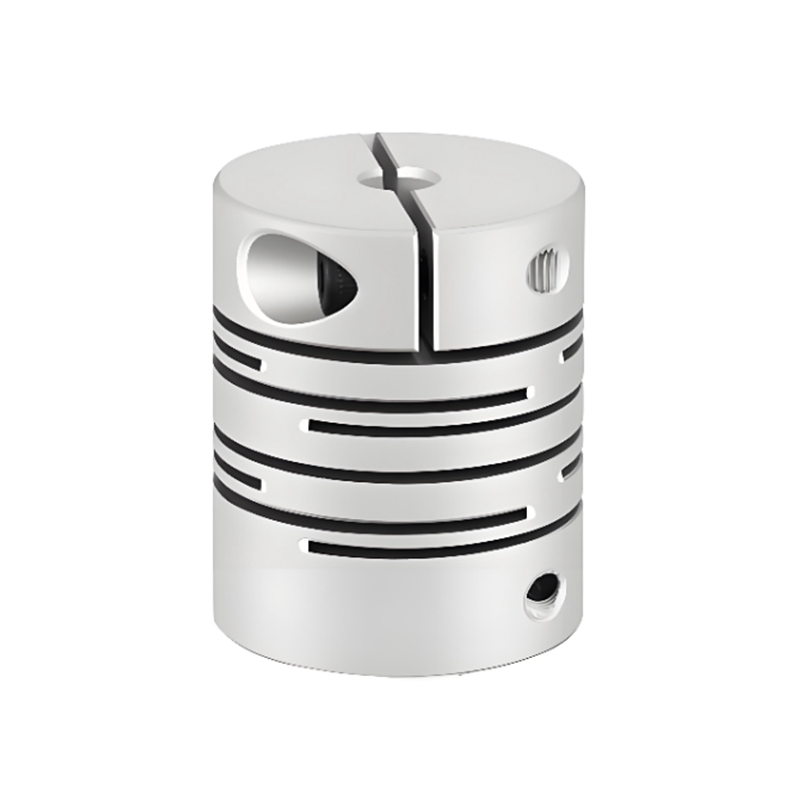
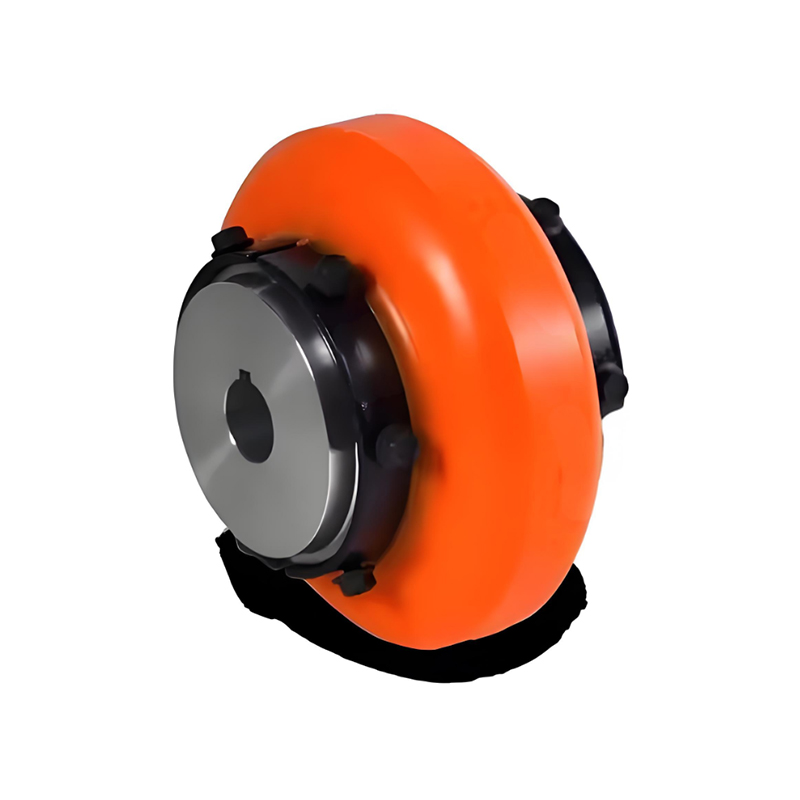
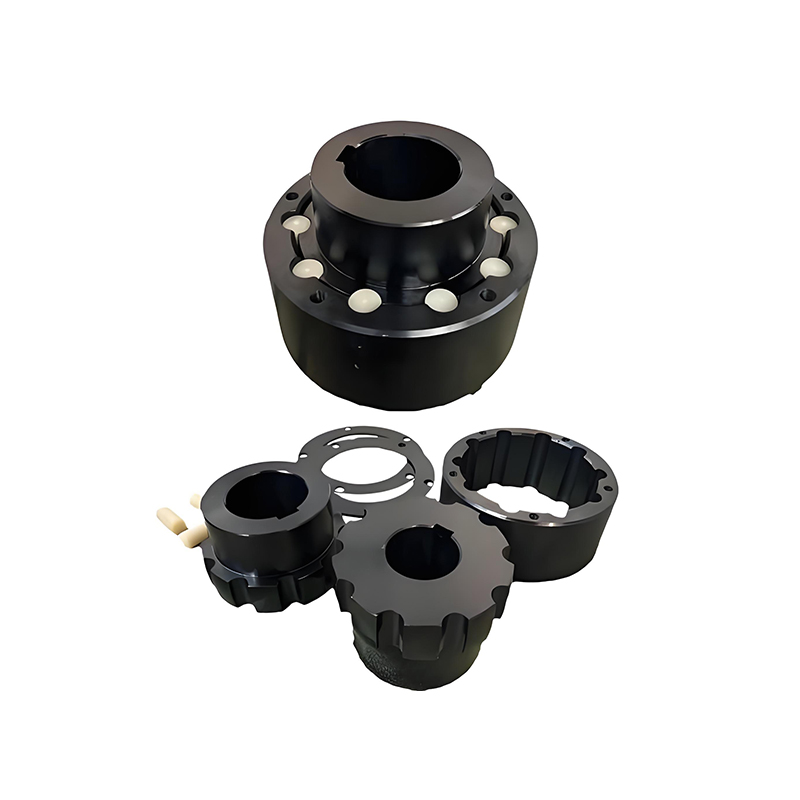
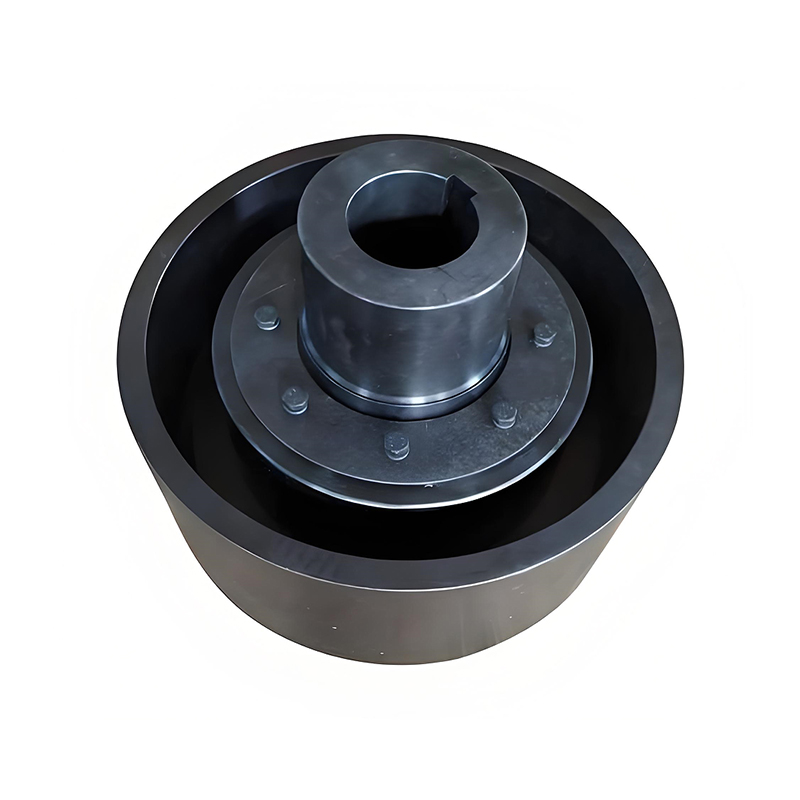
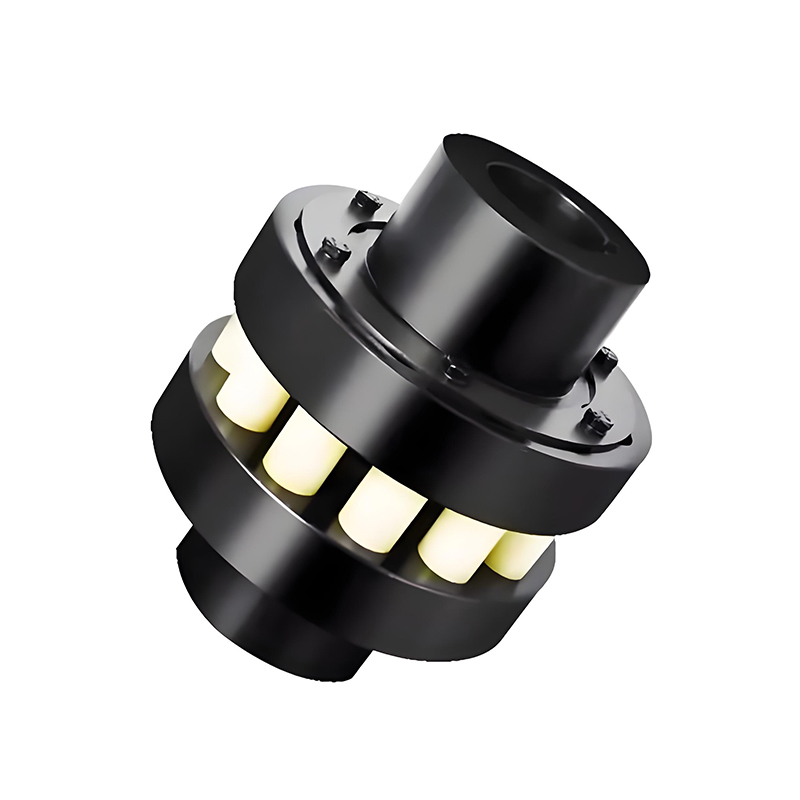
A flexible coupling connects two shafts to transmit torque while compensating for minor misalignments (angular, parallel, axial), dampening vibrations, and absorbing shock, preventing damage to machinery like motors and pumps, and improving system longevity, with types ranging from elastomeric jaw couplings to metallic gear or diaphragm couplings.
What it does
Transmits Power: Connects two rotating shafts to move power from a driver (like a motor) to a driven component.
Accommodates Misalignment: Allows for slight imperfections in shaft alignment (angular, parallel, axial) that are common in real-world machinery.
Dampens Vibration & Shock: Absorbs torsional vibrations and shock loads, reducing wear on bearings and other parts.
Provides Protection: Can act as a "mechanical fuse" to fail before more expensive components break during severe overloads.
Key benefits
Reduces Downtime: Prevents premature failure by handling dynamic operating conditions.
Enhances Performance: Improves accuracy and lifespan of connected equipment.
Versatile: Many designs cater to specific needs, from high-speed precision to heavy-duty industrial tasks.
Common types
Jaw Couplings: Use elastomeric inserts (like spiders) for shock absorption, common in electric motors.
Gear Couplings: High torque capacity, using external/internal gear teeth for flexibility.
Diaphragm Couplings: Transmit torque via thin metal diaphragms, good for high speeds.
Pin & Bushing: Simple, cost-effective design using rubber bushes.
Tire Couplings: Feature a rubber tire element that provides high torsional flexibility, ideal for systems with significant misalignment or impact loads.
Applications
Industrial power transmission (pumps, conveyors).
Robotics and automation.
CNC machinery.
HVAC systems.
How they work (Example: Jaw Coupling)
Two hubs connect to each shaft.
An elastomeric insert (spider) sits between them, often with curved jaws.
Torque is transmitted through the insert, which flexes to manage angular, parallel, or axial misalignment, while dampening vibrations.




 English
English русский
русский





















